One of the most astounding discoveries of recent times is just how much influence gut bacteria have on our health and well-being. In addition to extracting nutrients from food, the collective activity of these tiny organisms protects people from infection and regulates the immune system. However, changes in the gut microbiota have been implicated in diseases ranging from obesity and diabetes to inflammatory bowel disease and cancer.
In a study published this month in the Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, researchers led by a team from Osaka University have found that the RA gut metagenome of the Japanese population had interesting characteristics and a population-specific pathway link with the host genome.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a common autoimmune disorder causing painful inflammation and damage to the joints of affected patients. Researchers have so far linked a whole host of genetic and environmental factors to the onset of rheumatoid arthritis, with the microbiota recently emerging as a possible contributing factor. However, while overstimulation of the immune response by specific bacteria has been implicated in the development of rheumatoid arthritis, the way in which the microbiota as a whole contributes to the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis remains the subject of much debate.
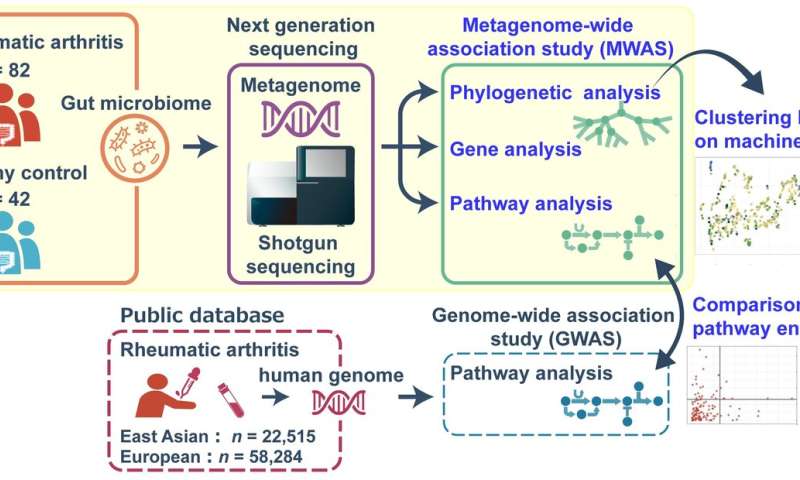
“We carried out a genetic screen using whole-genome shotgun sequencing of the entire gut microbial community in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and compared it to that of healthy controls to get a better idea of which bacterial species, genes, and pathways may contribute to the onset of rheumatoid arthritis in Japanese patients,” explains lead author of the study Toshihiro Kishikawa.
This screen, called a metagenome-wide association study (MWAS), showed an abundance of various bacteria belonging to the genus Prevotella in the gut microbiota of rheumatoid arthritis patients, indicating that more species than were previously thought may be involved in disease etiology. In addition, the study identified several genes and biological pathways that were significantly enriched in the rheumatoid arthritis metagenome.
“We then compared the enriched pathways in the bacterial metagenome with those shown to be enriched in the genomes of East Asian and European patients with rheumatoid arthritis,” says senior author of the study Yukinori Okada. “Interestingly, while several overlapping pathways were identified between the metagenome and the host genomes, the correlation was only significant for the East Asian population, suggesting a population-specific link between the host genome and the metagenome in the pathology of rheumatoid arthritis.”
Source: Read Full Article