Severe acute COVID-19 is very rare in children, but SARS-CoV-2 infection can trigger a novel post infectious condition called Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C). MIS-C is a potentially serious condition, and so far, little has been known on risk factors for developing MIS-C.
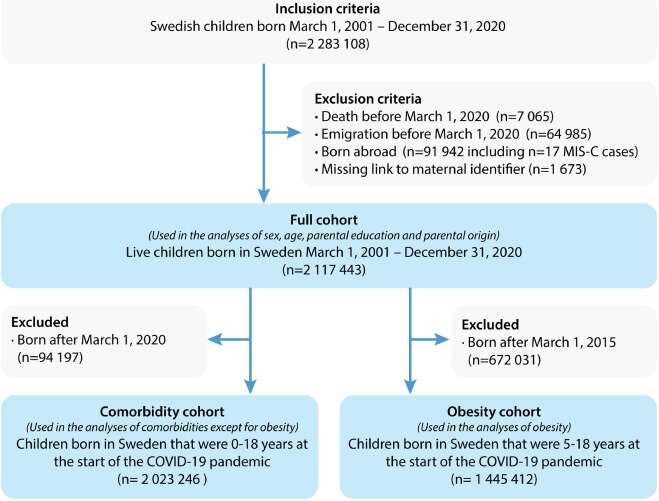
With that in mind, a large Swedish population-based cohort study was conducted by researchers at Karolinska Institutet, including more than two million Swedish children and adolescents <19 years. Sex, age, parental region of birth, parental education, asthma, autoimmune disease, chronic heart disease, chronic lung disease, obesity and life-limiting conditions were assessed as risk factors. Data were retrieved from national health and sociodemographic registers and information on the outcome MIS-C was retrieved from the Swedish Pediatric Rheumatology Quality Register for the period March 1, 2020–December 8, 2021. Hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated using Cox regression analysis. Incidence rates per 100,000 person-years were calculated assuming a Poisson distribution.
The study, which was recently published in The Lancet Regional Health—Europe, shows that among the 2,117,443 children, 253 children developed MIS-C, corresponding to an incidence rate of 6.8 (95% CI: 6.0–7.6) per 100,000 person-years. Male sex (HR 1.65, 95% CI: 1.28–2.14), age 5–11 years (adjusted HR 1.44, 95% CI: 1.06–1.95 using children 0–4 years as reference), foreign-born parents (HR 2.53, 95% CI: 1.93–3.34), asthma (aHR 1.49, 95% CI: 1.00–2.20), obesity (aHR 2.15, 95% CI: 1.09–4.25) and life-limiting conditions (aHR 3.10, 95% CI: 1.80–5.33) were identified as risk factors for MIS-C. In contrast, adolescents 16–18 years of age, had a decreased risk for MIS-C (aHR 0.45, 95% CI: 0.24–0.85).
Source: Read Full Article